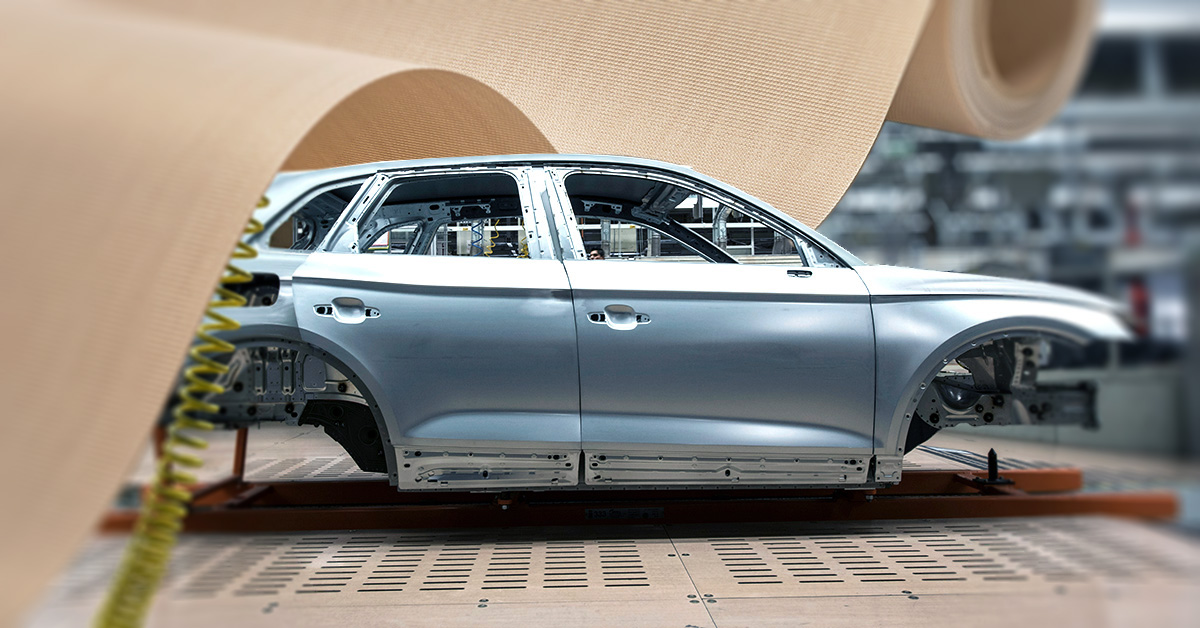
Versiv Products of Choice for Molding of Automotive Parts
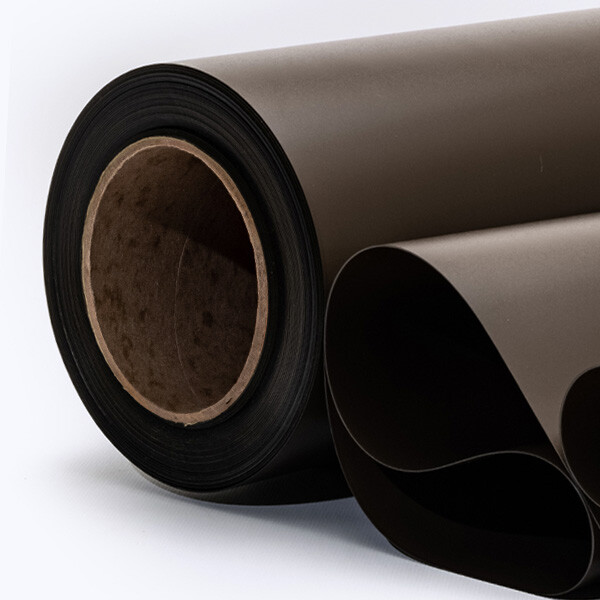
Thin PTFE-coated glass fabric. Mainly used as reliable release sheet with lower demand on mechanical strength.
PTFE-coated fabric tape with excellent mechanical strength and silicone pressure adhesive with clean release performance. Ideal for mold release cover.
Heavily PTFE-coated, strong release fabric for sheet or belting applications with high strength requirements.
Flexible skived PTFE film tape to cover splice areas. No fibreglass core.
Conclusion
Mold release materials play a vital role in reducing waste, improving quality, and supporting sustainability in automotive manufacturing. By enabling the use of advanced composites and recycled materials, these solutions help manufacturers meet both operational and environmental goals.
Supporting regulatory compliance and circularity
As regulations tighten, the ability to produce lighter, recyclable components becomes more urgent. Mold release fabrics make it feasible to incorporate recycled fibers and resins into automotive parts, supporting closed-loop manufacturing and compliance with environmental mandates.
In some automotive applications—especially those focused on noise, vibration, and harshness—recycled materials like polyester can only be used because mold release sheets make them workable during manufacturing.
The risks of inconsistent release: Reputational and financial costs
According to Auto World Journal, around 5.6 million tonnes of plastic automotive waste is produced each year, although the industry has worked hard to reduce waste
It is a simple equation in composite part manufacturing. Without consistent, reliable release from the mold, or if the release fails or degrades prematurely, waste gathers. This can result in defective parts, increased downtime or more regular replacement of release materials.
Manufacturers want to avoid a situation where release is not given or doesn’t last as long as forecasted. What is required are materials that offer persistent release until expiry, a longer and more predictable length of time of usage from those materials. The longer it lasts, the less scrap they produce in both cases.
Predictability is crucial: manufacturers only discover a release material’s end of life when scrap begins to appear. The longer the material performs, the less waste is generated—both in defective parts and in the release material itself.
In addition to the rising costs of disposal and the complexities of waste management, excessive waste poses a significant reputational risk in today’s era of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards—particularly among environmentally conscious consumers and partners.